Soft Deletes
Last Updated 1/3/2024
INTRODUCTION
Soft deletes refer to a data management technique where instead of permanently removing records from a database, the data is marked as deleted or archived without actually eliminating it. This approach is commonly used to retain historical data, facilitate data recovery, and maintain data integrity. Here are some main topics related to soft deletes.
- Enable Data Recovery: Allow for the restoration of accidentally deleted data.
- Maintain Historical Tracking: Retain a historical audit trail of changes over time.
- Preserve Data Integrity: Avoid complete removal to maintain relationships and dependencies.
- Comply with Regulations: Meet regulatory requirements by retaining specific data.
- Mitigate User Errors: Act as a safety net against unintentional data loss.
- Integrate with Business Logic: Support business workflows and logic by marking records as inactive.
- Enhance Auditing: Provide transparency on who performed deletions and when.
- Prevent Cascade Deletions: Stop cascading deletions in systems with relational databases and foreign key constraints.
- Improve User Experience: Boost user confidence by allowing data recovery.
- Facilitate Archiving: Support efficient storage and retrieval of archived information.
Soft deletes involve marking records as deleted instead of permanently removing them from a database. In contrast, hard deletes permanently remove data, resulting in irreversible loss and potential compliance challenges. The choice depends on recovery needs and regulatory considerations, with soft deletes offering a flexible approach.
IMPLEMENTAION
Implementing soft deletes involves incorporating mechanisms into a database system to mark records as deleted without physically removing them. The specific steps can vary based on the database management system (DBMS) and the overall architecture of the application. Here's a general guide on implementing soft deletes:
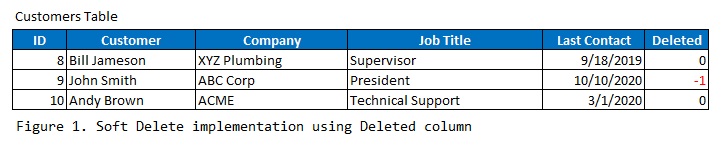
Add a Deleted Flag
Introduce a new column in the database table, typically named "deleted" or a similar term. This column is usually a boolean (true/false) or an integer (0 for not deleted, -1 for deleted).
ALTER TABLE Customers
ADD COLUMN Deleted BOOLEAN DEFAULT 0;
Update Data Access Logic
Modify your application's data access logic (queries, CRUD operations) to consider the "deleted" flag. Include the "deleted" condition in queries to exclude soft-deleted records by default.
SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE Deleted = 0;
Soft Delete Records
When a record needs to be deleted, update the "deleted" flag instead of executing a hard delete.
UPDATE Customers SET Deleted = -1 WHERE ID = your_record_id;
Restore Soft-Deleted Records
To restore a soft-deleted record, update the "deleted" flag back to its original state.
UPDATE Customers SET Deleted = 0 WHERE ID = your_record_id;
Handle Relationships
If your database has relationships between tables, consider how soft deletes impact these relationships. Adjust foreign key constraints or cascade options as needed to maintain data integrity.
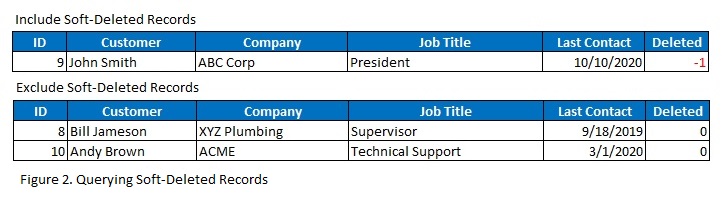
Include Deleted Records in Reports
Modify reporting queries to include or exclude soft-deleted records based on the reporting needs.
-- Include soft-deleted records in a report
SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE Deleted = -1;
-- Exclude soft-deleted records in a report
SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE Deleted = 0;
Implement Audit Trails
Create mechanisms to log soft delete events, including who performed the deletion and when. This audit trail can be valuable for tracking changes and maintaining accountability.
-- Example soft delete operation and audit trail insertion in SQL
UPDATE Customers SET Deleted = -1 WHERE ID = your_record_id;
INSERT INTO audit_trail (user_id, operation_type, timestamp)
VALUES (performing_user_id, 'soft_delete', current_timestamp);
Consider Indexing
Depending on the size of the dataset, consider indexing the "deleted" column to optimize query performance.
CREATE INDEX idx_deleted ON Customers (Deleted);
Purging Mechanism
Implement a purging mechanism to permanently remove soft-deleted records after a defined retention period if needed.
Document Soft Delete Policy
Clearly document the soft delete policy, including how it affects data access, recovery procedures, and any related business rules.
CHALLENGES
While soft deletes offer several benefits, they also come with certain challenges that organizations need to consider during implementation and ongoing maintenance. Here are some challenges associated with soft deletes.
Increased Storage Requirements
Soft deletes can contribute to increased storage requirements over time, especially in systems with a high frequency of data modifications. The historical retention of deleted records may lead to larger databases.
Query Performance
Including a "deleted" flag in queries can impact query performance, particularly if not properly indexed. Queries may need optimization to maintain acceptable response times.
Complexity in Data Access Logic
Soft deletes introduce complexity to data access logic, as queries must include conditions to filter out deleted records. Developers need to be vigilant in ensuring that these conditions are consistently applied.
Cascading Deletes in Relationships
Soft deletes do not prevent cascading deletes in relationships by default. Managing foreign key constraints and preventing unintended data loss in related tables requires additional consideration and effort.
Data Purging Strategies
Establishing effective data purging strategies is crucial. Soft-deleted records may need to be purged periodically to avoid excessive storage consumption, and defining the right criteria for purging can be challenging.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Soft deletes may pose security and privacy concerns, especially when dealing with sensitive or personally identifiable information. Even though records are marked as deleted, they still exist in the system and need to be handled securely.
Audit Trail Maintenance
Maintaining accurate and comprehensive audit trails for soft deletes requires additional effort. Tracking who performed deletions and when is essential for security and compliance but can be resource-intensive.
User Education and Expectations
Users must be educated about the nature of soft deletes and understand the implications. They need to be aware that marking a record as deleted does not immediately remove it from the system, and there may be a delay before data is purged.
Backup and Restore Considerations
Backup and restore processes may need to be adjusted to account for soft-deleted records. A comprehensive backup strategy should include the ability to restore both active and soft-deleted data.
Consistency Across Systems
Ensuring consistency across multiple systems or services, especially in microservices architectures, can be challenging when implementing soft deletes. Synchronization mechanisms may be necessary.
Implementation Overhead
Implementing soft deletes requires additional steps in the development process, including modifying data access logic, creating audit trails, and establishing purging mechanisms. This can add implementation overhead.
Undo Mechanism Complexity
Implementing an undo mechanism for soft deletes can be complex and may require careful design and consideration of business logic.
Despite these challenges, many organizations find that the benefits of soft deletes, such as data recovery, historical tracking, and compliance, outweigh the challenges associated with their implementation. Careful planning and ongoing maintenance practices are key to mitigating these challenges effectively.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, soft deletes provide a flexible and user-friendly approach to managing data in a database system. By marking records as deleted without permanent removal, soft deletes offer benefits such as easy data recovery, maintenance of data integrity, and historical tracking. This approach is particularly valuable for safeguarding against accidental deletions, complying with data retention regulations, and fostering a positive user experience. However, organizations should carefully consider factors like security, compliance, and system performance when implementing soft deletes. Striking a balance between data protection and operational efficiency is essential to leverage the advantages of soft deletes effectively.